Get called
Demonstration
To process your request, we need to process your personal data. Find out more about the processing of your personal data here.
August 1, 2024 marks an important date for businesses and digital professionals in France, with the entry into force of the Artificial Intelligence Regulation (AIR).
This regulation, adopted by the European Union, aims to regulate the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in commercial, industrial and social activities, in order to guarantee safety, ethics and transparency in the use of these technologies.
In this article, we decipher these new regulations for you, share everything you need to know, and suggest the best practices to adopt to ensure your compliance.
The Artificial Intelligence Regulation (AIR ) is a legislative framework drawn up by the European Union to regulate the application and development of AI. This regulation is part of a broader drive to make Europe a world leader in artificial intelligence, while protecting citizens' fundamental rights.
The RIA is based on a risk-based approach, categorizing AI systems into four levels of risk: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal. Each category is subject to specific rules, designed to ensure a balance between technological innovation and the protection of human rights.
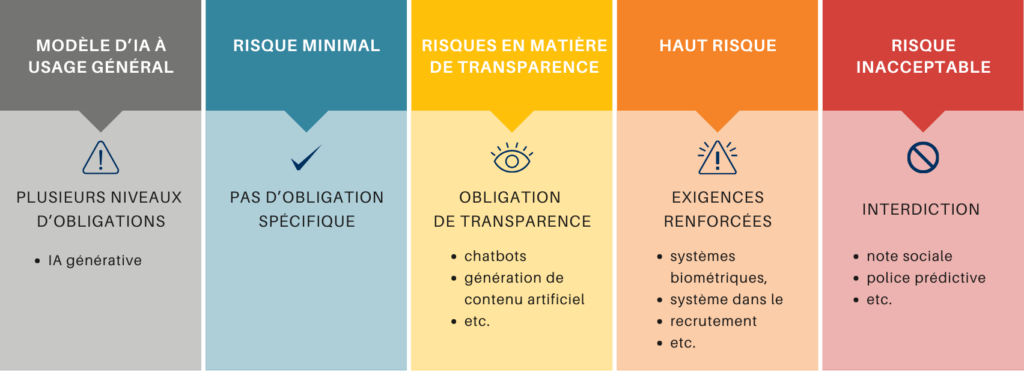
Artificial intelligence is at the heart of digital transformation. However, without adequate regulation, it can present significant risks, particularly in terms of discrimination, privacy violations and security. The RIA therefore responds to the need to establish a clear framework for the use of AI, guaranteeing that its development is carried out ethically and transparently.
This regulation is crucial for :
Two types of governance :
At European level:
At national level: France has 12 months to define one or more control authorities.
In the event of non-compliance, the RIA imposes a market withdrawal or product recall, as well as administrative fines of up to 35 million euros or 7% of annual worldwide sales.
NO: The GDPR concerns any processing of personal data, whereas the RIA concerns the development, marketing and deployment of AI.
Although the RIA and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR ) are both European legal frameworks, they aim to regulate different aspects of digital.
| RIA | GDPR | |
|---|---|---|
| Effective date | August 1, 2024 | May 25, 2018 |
| Scope of application | AI development, commercialization and deployment | Any processing of personal data (including for the purpose of developing or training an AI) |
| Approach | Risk-based approach: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal. | Approach based on the application of key principles, risk assessment and Accountability |
| Target players | Mainly suppliers and deployers of AI systems | Processing managers and processors |
| Conformity assessment | Internal or third-party assessment through a risk management system | Accountability principle (legal documentation in-house) and compliance tools |
| Control authority | Not yet defined | CNIL (National Commission for Information Technology and Civil Liberties) ) (Commission nationale de l'informatique et des libertés) |
| Sanctions | Market withdrawal or product recall + administrative fines of up to 35 million euros or 7% of worldwide annual sales . | Formal notice + administrative fines of up to 20 million euros or 4% of worldwide annual sales . |
🔍 Here are four possible scenarios:
1️⃣ RIA only: RIA only applies when, for example, a high-risk AI system is used without involving the processing of personal data.
2️⃣ GDPR only: The GDPR applies in situations where personal data is processed, but the AI system used is not subject to the requirements of the RIA.
3️⃣ RIA and GDPR combined: The two regulations apply in conjunction when, for example, a high-risk AI system requires personal data for its development or implementation.
4️⃣ Neither applies: Neither the RIA nor the GDPR are required in cases where an AI system presents minimal risk and does not process personal data.
The coming into force of the RIA requires companies to review their AI processes and systems to ensure compliance with the new regulations.
For you as a company, it's an opportunity to strengthen your credibility and competitiveness in the marketplace by adopting practices that comply with European expectations.
Here are 4 best practices to implement right now:
As an external DPO, Dippeo offers its clients
The Artificial Intelligence Regulation (AIR) represents a turning point for the AI industry in Europe, imposing high standards in terms of safety and respect for human rights. Its entry into force on August 1, 2024 is a key step towards a more responsible and ethical use of artificial intelligence.
For companies, this means not only a need to adapt quickly, but also an opportunity to strengthen their credibility and competitiveness in the marketplace by adopting practices that comply with European expectations. The future of AI is promising, but it's up to economic players to embrace it safely and responsibly.